ATMS is a transport service that provides reliable and secure delivery of data, voice, and video content in packets referred to as ATM cells. These cells (composed of 53 byte fixed length containers) are delivered via links between ATM switches to comprise a network. ATMS may be delivered as Native ATM or as Emulated ATM but not both, depending on the Agency's requirements. The service footprint covers CONUS, OCONUS, and Non-Domestic locations. The service's performance and reliability in delivering converged data, video and voice applications, makes it an attractive alternative to Private Line or Frame Relay (FR) networks.
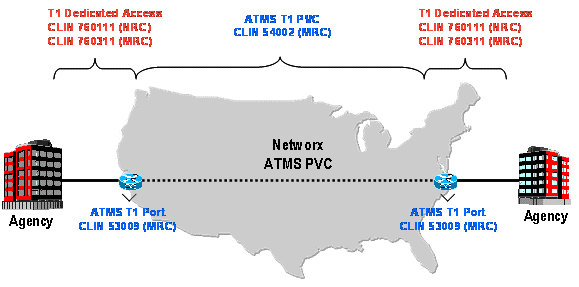
The example shown below illustrates some of the key technical requirements satisfied by ATMS. Agencies with both Routine and Critical Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are connected to the contractor's backbone network through contractor-provided access services that include dial-up Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), Ethernet, Frame Relay Service (FRS), Private Line Service (PLS), other Agency ATMS, and dial-backup. ATMS can accommodate connections at customer locations via Agency's routers, ATM edge switches, multiplexing/switching devices, PBXs, and host computers. Critical Agency locations requiring high availability may purchase multiple edge switches to provide switch diversity. Inverse Multiplexing capability for ATM (IMA) can provide a scalable and cost-effective solution for customers who choose to optimize WAN resources among existing T1s (NxDS1), without having to purchase DS3 or OC3 circuits.

The ATMS solution provides a connection-oriented, transmission service with scalable port speeds of DS-1, DS-3, OC-3, and OC-12. In addition, ATMS provides E-1 and E-3 port speeds for terminations outside the United States. ATMS provides service continuity to FTS2001 contracts.
ATMS supports the following technical capabilities as described in Section C.2.3.2.1.4 of the Networx contracts:
ATMS allows Agencies to interconnect sites served by ATMS, FRS, PLS, and Ethernet services. Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is an enhancement to IP/ATM networks that is offered on ATMS. An MPLS backbone creates virtual circuits between MPLS-enabled endpoints on the network in order to speed up connections.
ATMS features are described in Section C.2.3.2.2.1 of the Networx contracts that include:
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for ATMS. The specific details can be found within each Contractor's Networx contract files and pricing notes for ATMS.
For more information on the general ATMS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.3.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.3.2 for pricing.
ATMS provides connection-oriented data transmission, between user locations, with scalable port speeds of DS-1, DS-3, OC-3, and OC-12. PVCs are distinguished by simplex versus duplex and by bit rate type:
ATMS is similar to the ATM Service offered on FTS2001 contracts.
Price components required for full end-to-end service for CONUS, OCONUS, and Non-Domestic ATMS:
* Some or all price components are priced on an Individual Case Basis (ICB). CLINs with ICB prices are not available in the unit pricer.
Each Networx contractor may provide variations or alternatives to the offering and pricing for ATMS. The specific details can be found within each Contractors Networx contract files and pricing notes for ATMS.
For more information on the general ATMS specifications and requirements, please refer to Section C.2.3.2 of the Networx contract for technical specifications and Section B.2.3.2 for pricing.